3 Options for Heating Automotive Headlights to Ensure Optical Camera Safety
3 Approaches; One Goal: Automotive Safety
Today's automobiles are loaded with sophisticated safety features meant to keep passengers safer than ever before. While some safety features are elective, others are mandated by the governmental agencies or industry consortiums. Automotive product designers and engineers need to balance safety requirements with the overall look and feel of the car, plus their choice of technological approach can have ensuing, negative implications. In this blog we will touch on 3 different approaches used in contemporary automotive safety systems and the implications of each technological approach.
1. Microwire Heated LED Headlights
Heat has been successfully used to control both ice and condensation in the automotive industry for years. As LED headlamps began increasing in popularity, both OEM and aftermarket companies recognized a market need for clearing ice and condensation from these cold running light sources. Several companies combine microwire heating elements into LED headlights lenses to facilitate clearing. While this technological approach is mature and effective, it can have two implications that can be perceived as negative. The first is that microwire is visible to the eye. The heating element pattern can be unique and distinctive, but for automakers looking to have technology “felt but not seen”, this represents a limitation. The second consequence is that both radar and lidar can be quite sensitive to any obstructions. If the headlamp is also to include collision avoidance systems, the microwire itself may cause issues with the performance of these safety systems.
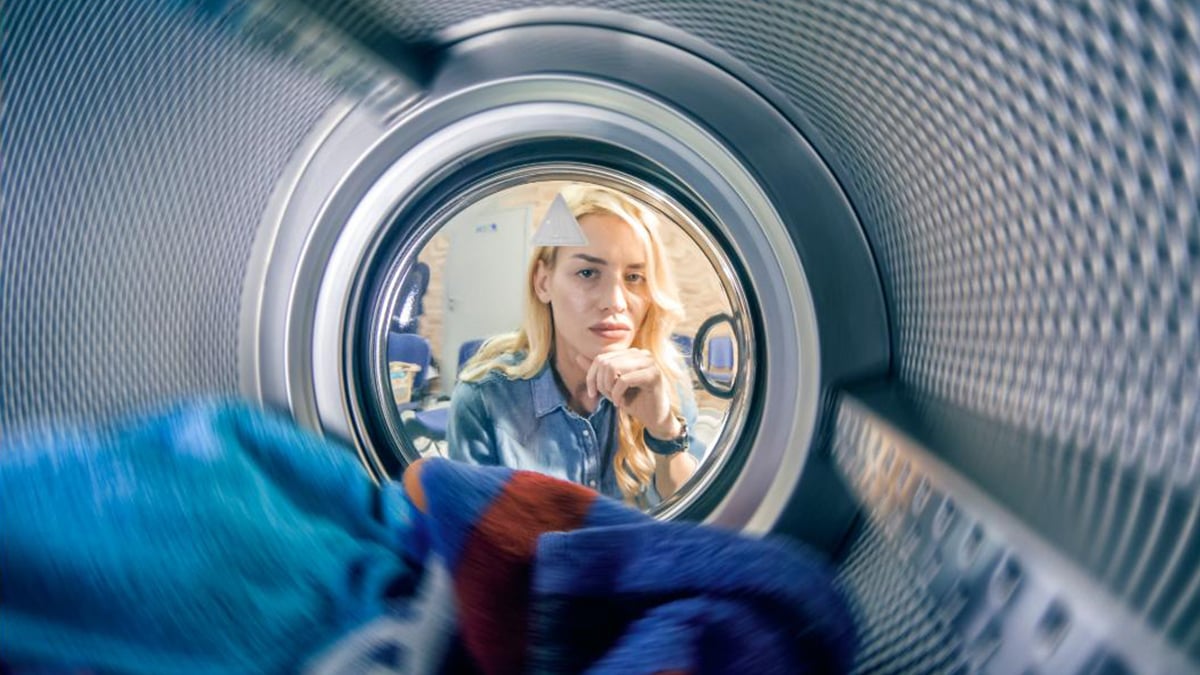
2. Optical Cameras Located in the Cabin
Optical cameras are gaining in acceptance as an excellent means of enabling emergency braking systems. They can assist with not only braking, but also for adaptive cruise control, maintaining a vehicle within a designated lane, and as a safeguard against distracted driving. These are highly sensitive cameras and control systems enable them to excel at their duties, however, this means that they cannot be obstructed by any kind of ice, snow, condensation or conductive heating element of any kind. Due to the criticality of their operation, designers have naturally placed these cameras inside the cabin, near the rear-view mirror such as Subaru's Eyesight. While effective, placement of the cameras is limited to an area providing the required field of view and one that does not negatively impact the driver’s field of view. Many states already have existing legislation banning the placement of articles or devices on the windshields of vehicles.

Image above: windshield mounted cameras. Enhanced safety comes with a footprint.
3. Transparent Heaters for LED Headlights or Optical Cameras
When esthetics or placement dictate a location subjected to extremes in weather, another option is to apply heat transparently. A new class of transparent conductive films – CNT Hybrids – can deliver a uniform heating pattern on a flexible and formable substrate at greater than 90% VLT. This can enable the automotive product designers and engineers to place camera or safety features in any convenient location on the car without concern for icing or condensation. Automotive designers may prefer this method as it enables greater design freedom while simultaneously offering engineers another technological approach to solving functional issues potentially caused by those same design choices - all while remaining compliant with safety laws.

.jpg)